Summary
Safety light curtains are advanced electro-sensitive protective devices used primarily in industrial settings to enhance personnel safety around hazardous machinery. These systems operate by emitting a series of infrared light beams from a transmitter to a receiver, forming a protective barrier that detects the presence of individuals or objects in a designated area. When an object interrupts the light beams, the safety light curtain sends a stop signal to the machinery, halting operations to prevent accidents and injuries.
The importance of safety light curtains stems from their critical role in workplace safety, particularly in high-risk environments such as manufacturing, automotive, and robotics. These devices not only help comply with safety regulations, such as those set forth by OSHA and ANSI, but also contribute to increased operational efficiency by allowing for seamless integration into automated systems. Features like muting functionality allow for specific objects to pass through the detection field without triggering a shutdown, optimizing workflow while maintaining safety standards.
Despite their advantages, safety light curtains are not without limitations. Issues such as high installation costs, vulnerability to environmental interference, and the need for thorough risk assessments pose challenges for organizations. Furthermore, specific types of light curtains may not be suitable for extremely high-risk environments, necessitating careful selection and installation based on safety categories and performance levels defined by standards like ISO 13849 and IEC 61496.
The ongoing evolution of safety light curtains is influenced by emerging technologies such as Al and loT, which promise to enhance their effectiveness and adaptability. As industries increasingly focus on safety and efficiency, the demand for these systems is expected to rise, particularly in sectors like automotive manufacturing and logistics, where collaborative robotics are becoming more prevalent.
Table of Contents
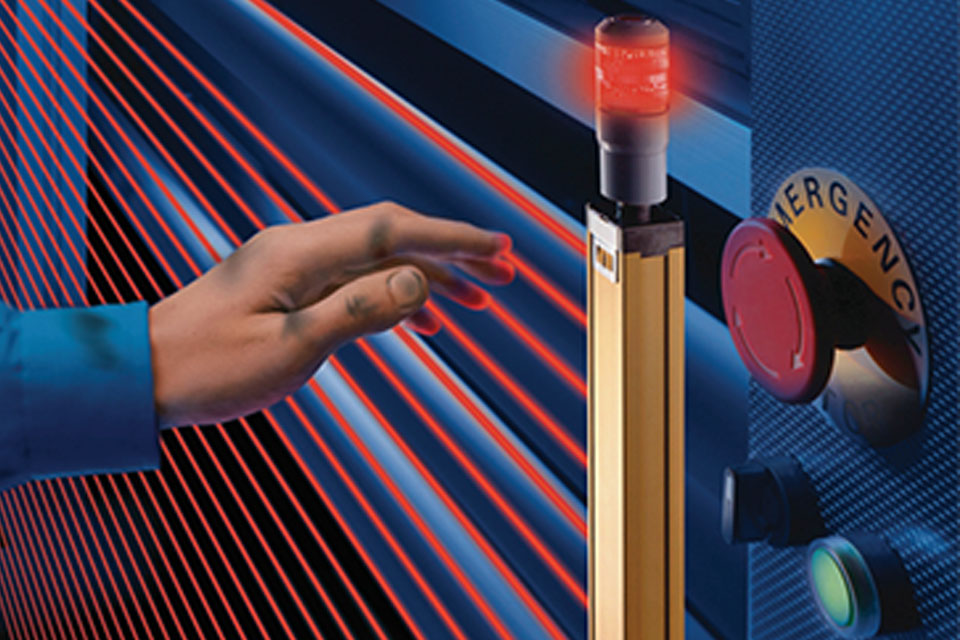
Principles of Operation
Safety light curtains function as presence detection devices designed to enhance safety in industrial environments. They typically consist of a pair of units: a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits an array of infrared light beams towards the receiver, which contains photoelectric cells. When an object interrupts one or more of these beams, a stop signal is sent to the machinery being safeguarded, effectively halting operations to prevent accidents.
Light Beam Detection
The operational principle of light curtains relies on the creation of a two-dimensional detection field, often referred to as a protective field. This field is established by a series of parallel light beams emitted from the transmitter to the receiver. The beams are sequenced and pulsed at a specific frequency, which helps the receiver to distinguish the signals from its dedicated transmitter, thereby filtering out unwanted light sources. This design ensures high reliability and precision in detecting objects, even in challenging conditions such as bright ambient light.
Response Time and Safety Distance
When an object disrupts the light beams, the light curtain initiates a safety response, which involves a brief response time. This time, typically ranging from 20 to 50 milliseconds, is crucial as it determines how quickly the machine can react to the detected presence of a person or object in its hazardous zone. Safety distance calculations, based on the stopping time of the machine and the light curtain’s response time, are essential to ensure adequate protection. Various formulas, such as those provided by OSHA and ANSI, guide the determination of these safety distances, which are critical for maintaining workplace safety.
Integration with Automation Systems
Safety light curtains can also be integrated with automation systems to streamline processes. By utilizing features such as muting functionality, which allows certain objects to pass without triggering a safety response, manufacturers can optimize workflow while maintaining safety standards. This flexibility makes light curtains a popular choice in environments where semi-automated procedures are commonplace. Moreover, the combined use of light curtains for both safety and automation tasks can lead to increased system throughput and reduced costs, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
Components
Overview of Safety Light Curtains
Safety light curtains are composed of a series of essential components that work together to create a protective barrier around hazardous machinery. Typically, these systems include a transmitter, a receiver, and various connection interfaces to ensure proper functionality within industrial environments.
Transmitter and Receiver
Transmitter
The transmitter is responsible for emitting a series of infrared light beams across a designated area. These beams are sequenced and pulsed at a specific frequency, allowing the receiver to recognize only the signals from its paired transmitter. This design minimizes the risk of interference from spurious light sources, enhancing safety and reliability.
Receiver
The receiver detects the light beams emitted by the transmitter. When an object or person interrupts the light beams, the receiver sends a signal to stop or slow down the machinery it protects. Modern safety light curtains often feature a seven-segment display and LED indicators that provide visual feedback regarding alignment, signal strength, and operational status, ensuring that operators can easily monitor the system’s performance.
Connection Interfaces
Safety light curtains typically connect to safety relays, which are critical for removing power from hazardous machinery upon detecting an obstruction in the light curtain’s beam path. These relays can include muting functionality, which allows for temporary disabling of the safety features, enabling objects to pass through without triggering a stop signal. This feature is particularly useful in applications involving semi-automated processes.
Design and Construction
According to IEC 61496-2:2020, safety light curtains must adhere to specific design and construction standards that ensure their effectiveness as electro-sensitive protective equipment (ESPE). This includes ensuring that they can detect human presence accurately while maintaining operational efficiency. Furthermore, ISO 13855:2010 provides guidelines for the positioning of these devices to optimize their effectiveness relative to human approach speeds, ensuring safety measures are appropriately implemented.
Installation
Assessment and Planning
Before the installation of safety light curtains, a thorough risk assessment should be conducted to identify hazardous areas and determine the appropriate type and configuration of safety curtains. The planning phase should also consider the layout of the machinery and the workflow of the operators to ensure optimal safety and efficiency in the workspace.
Installation Process
Safety curtains must be installed following the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety standards to ensure their effectiveness. Proper alignment of the emitter and receiver is crucial to ensure uninterrupted beam transmission. The safety curtains should be mounted at an appropriate height and distance from the hazardous area, providing adequate protection without hindering operations. The minimum mounting distance should never be closer than 6 inches from the hazard zone, even if calculations suggest a smaller distance.
Installation Tips
Several best practices can enhance the installation process:
- Secure Brackets: Utilize secure brackets and mounting equipment to ensure that the safety light barriers are firmly mounted and not susceptible to vibrations or external interference.
- Cable Installation: Pay attention to the installation of cables to prevent damage and ensure compliance with relevant electrical safety standards. Appropriate cable protection should be used to avert short circuits or other electrical problems.
- System Testing: A comprehensive system test should be performed prior to commissioning to verify the performance of the safety barriers. This includes checking that they accurately detect the entry of people or objects and trigger the necessary safety response.
Compliance with Standards
It is essential to comply with various safety standards during the installation of light curtains. In the United States, standards such as OSHA 29 CFR 1910.217 and ANSI B11.19 provide guidance on calculating safety distances and ensuring overall machine safety. International standards like ISO 13857 also inform proper placement and installation practices for light curtains.
Maintenance Considerations
Once installed, the maintenance of safety light curtains should be simple and efficient. Systems featuring self-diagnostic capabilities can significantly aid in maintenance efforts by identifying potential issues before they lead to failure. Regular checks and necessary repairs should be scheduled to ensure continued compliance and operational safety. If a light curtain is damaged, it may be removed for repair, and an OSHA-compliant point-of-operation safeguard should be temporarily installed to maintain worker safety during downtime.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Safety light curtains are subject to various standards and regulations that ensure their effectiveness in safeguarding machinery and protecting operators. These standards guide the design, installation, and maintenance of safety systems, particularly in high-risk environments like manufacturing.
Key Standards
ANSI Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards in the United States. For safety light curtains, ANSI B11.1 is particularly relevant, outlining safety requirements for mechanical presses. The latest revision, published in 2009, includes guidelines for new technologies such as direct-drive servo presses. ANSI B11.TR3 provides detailed procedures for conducting risk assessments, essential for determining appropriate safety measures in various applications.
IEC and ISO Standards
Internationally, several standards are crucial for the functional safety of light curtains: IEC 61508 establishes the requirements for the safety of electric and programmable electronic devices, ensuring they meet specific Safety Integrity Levels (SIL). ISO 13849-1 specifies requirements for Performance Levels (PL) for safety-related control systems in machinery, which applies directly to safety light curtains. IEC 61496 specifically addresses photoelectric devices, including light curtains, defining their design and performance requirements.
Safety Categories and Performance Levels
Light curtains are classified into categories based on their safety performance. For example, Category 4 corresponds to the highest level of safety, suitable for environments with significant risk, such as metal stamping operations. This categorization is integral to risk assessments, where factors like frequency of exposure and potential severity of injuries are evaluated.
Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing of safety light curtains is recommended to ensure their reliability. Best practices include conducting tests at the beginning of each shift or when there is a change in operators. These tests verify that the light curtain is functioning correctly and that it effectively communicates with the press to halt operations when necessary. Manufacturers often provide guidelines for these testing procedures, reinforcing compliance with safety standards. By adhering to these established standards and conducting proper maintenance, users can significantly mitigate risks associated with machinery operations, thereby enhancing workplace safety.
Applications
Safety light curtains are widely used in various industries to enhance operational safety and efficiency. These devices serve critical functions by ensuring the safety of personnel working in proximity to potentially hazardous machinery.
Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, safety light curtains are commonly installed in areas where automation processes occur. For instance, they are used in press machines to detect the presence of hands or other body parts when operators are loading or unloading workpieces, ensuring immediate cessation of operation if a person is detected within a dangerous zone. They also play a pivotal role in robotic systems, providing safety barriers that allow for efficient setup without the need to open and close safety doors, thereby optimizing workflow.
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive sector extensively utilizes safety light curtains to safeguard high-risk processes on vehicle assembly lines. With over 50% of automotive production plants incorporating these systems, they comply with industry safety standards while enhancing worker protection and operational efficiency. The integration of Al-led safety monitoring within these setups has further advanced safety compliance and reduced downtime by enabling real-time tracking and hazard detection.
Semiconductor and Electronics Industries
In the semiconductor manufacturing environment, safety light curtains are critical for maintaining safety while maximizing productivity. They are designed to be compatible with clean room standards, featuring dust-resistant enclosures and ultra-high precision beam alignment. This specificity is crucial in processes like high-speed PCB production and semiconductor packaging, where operational safety is paramount.
Food and Beverage Industry
Safety light curtains also find application in the food and beverage sector, where they monitor equipment operation to prevent food contamination and minimize waste. Their ability to ensure safe handling in high-traffic areas enhances both safety and operational efficiency.
Logistics and Warehousing
In logistics and warehousing, safety light curtains facilitate safe transportation of goods, particularly in environments where Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) navigate. These systems help in obstacle avoidance and ensure that safety protocols are adhered to during the movement of goods, thereby reducing the risk of accidents.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
Safety light curtains offer several advantages that make them an appealing option for safeguarding personnel in industrial environments. One significant benefit is their compact design, which allows for easier installation and integration into existing machinery setups. Additionally, they tend to be less expensive than traditional mechanical guarding solutions, providing a cost-effective means of ensuring safety without compromising operational efficiency. Light curtains can be tailored to specific applications, allowing for features such as blanking, which permits certain objects to pass through the protective field without triggering a shutdown, thereby enhancing productivity.
Moreover, the use of light curtains can improve accessibility to machinery, enabling operators to perform semi-automatic procedures more efficiently. This is particularly useful in environments where quick access is necessary, such as during the loading and unloading of parts. As technology advances, the integration of smart sensors and Al-powered safety analytics further enhances the effectiveness and adaptability of safety light curtains, making them suitable for a broader range of applications in industrial automation.
Limitations
Despite their advantages, safety light curtains also have limitations that must be considered. High installation costs can be a barrier for some organizations, particularly when factoring in calibration and integration with existing systems. Additionally, these devices are vulnerable to environmental factors such as dust, vibration, and electrical interference, which can lead to sensor malfunctions or false triggers, potentially resulting in operational inefficiencies.
Another critical limitation is related to the application of Type 2 safety light curtains. These devices are not suitable for high-risk environments where severe injuries could occur, such as on mechanical power presses, and they do not meet control reliability standards. Conducting thorough risk assessments is essential to determine the appropriateness of using Type 2 or Type 4 light curtains based on the specific risks involved. Furthermore, design flaws, such as incorrect beam heights or inadequate coverage of hazardous movements, can undermine their effectiveness, highlighting the importance of proper installation and adherence to standards like ISO 13855.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of safety light curtains are essential for ensuring their effectiveness and longevity. Regular maintenance helps prevent malfunctions and extends the lifespan of the equipment, directly impacting safety functions in various industrial applications.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Routine maintenance involves several key practices, including regular inspections, cleaning, and testing. It is recommended to assign dedicated personnel for the care of safety light curtains. Daily checks should include verifying that the safety grating is powered on and functioning properly before operating machinery. Cleaning is also crucial; the lenses of the emitter and receiver should be kept free from dirt and debris, which could impede their function. Additionally, the filter plate should be regularly cleaned to prevent the accumulation of oil stains and dust, and it may be beneficial to provide protective covers for the grating.
Preventive maintenance, which might involve slight disruptions in production, is vital to avoid more significant downtime caused by unexpected breakdowns. Documenting maintenance activities, including the procedures performed and any corrective actions taken, ensures compliance and accountability.
Troubleshooting Malfunctions
In the event of a malfunction, it is essential to identify possible causes and implement appropriate repair methods. Common issues may stem from problems with the control program or the electronics of the safety light curtain. In such cases, it is advisable to check the control system and, if necessary, reinstall or upgrade the control program. Regular visual inspections and functional tests should be conducted to verify proper operation. If any faults are identified, they should be addressed promptly to maintain the integrity of the safety system.
In some instances, specific light beams in a safety curtain may need to be deactivated to allow objects of predetermined sizes to pass without interrupting the machine—a process known as blanking. This requires careful configuration to ensure the safety of the operational area.
Professional Support
For those who may encounter complexities beyond basic troubleshooting, seeking professional technical support is recommended. This can provide additional insights and solutions, particularly in intricate operational environments where safety is paramount. Regular training and updates for personnel on maintenance procedures and troubleshooting techniques are also beneficial for maintaining a safe workplace.
Future Trends
The safety light curtain market is poised for significant evolution driven by several key trends that align with the increasing integration of Industry 4.0 technologies and heightened workplace safety awareness. One notable advancement is the rise of predictive maintenance systems, which enable safety light curtains to monitor their own performance and notify operators of potential issues before they lead to failure, enhancing operational reliability and safety.
Technological Advancements
A critical factor in the future of safety light curtains is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. These advancements facilitate real-time monitoring, dynamic safety zone management, and improved object recognition capabilities, allowing for smarter and more responsive safety systems. For instance, Al-driven safety solutions can adaptively control safety zones based on the presence and movement of personnel, thus ensuring optimal protection as work environments change.
Market Growth and Adoption
As industries increasingly prioritize worker safety and regulatory compliance, the demand for advanced safety light curtains is expected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as automotive and semiconductor manufacturing, where automated safety solutions are becoming standard to mitigate risks associated with hazardous machinery. Moreover, the market is projected to experience robust growth in the Asia-Pacific region, driven by rapid industrialization and rising investment in manufacturing technologies.
Integration with Collaborative Robotics
The transition towards collaborative robotics (cobots) is another trend influencing the future of safety light curtains. These robots often operate alongside human workers, necessitating enhanced safety measures. High-resolution safety light curtains are being utilized to protect both the robots and their human counterparts, ensuring that safety protocols can keep pace with the evolving nature of industrial work.
Focus on Compliance and Sustainability
In response to stringent workplace safety regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, manufacturers are innovating to produce energy-efficient safety solutions that comply with modern standards. Enhanced designs that feature dust-resistant enclosures and anti-static housings, particularly for clean room applications, are becoming more prevalent. This focus on sustainability is likely to shape product development in the coming years.
















